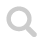Carbon monoxide has a small linear molecule with a relatively short C-O bond, earlier described as a double bond but nowadays mostly as a triple bond. The valence electrons are slightly drawn towards oxygen, which makes the molecule polar.
Carbon monoxide molecule shown in two ways, from Wikipedia. The C-O triple bond has the unit pm (picometer) which means 10⁻¹² m.
CO is an uncolored and non-smelling gas at room temperature. Carbon monoxide is highly toxic since it replaces O₂ molecules in hemoglobin, causing suffocation after a short while, and the state continues even after a poisoned person is taken into fresh air. Carbon monoxide is flammable and easily forming CO₂ in this reaction: 2CO(g) + O₂(g) → 2CO₂(g) The gas is found in all types of burning, for example car exhaust gases or smoke from a fire. It is also found in cigarette smoke. Moreover, it has been used in wartime for killing people.
IR spectrum of carbon monoxide, CO
The IR spectrum of carbon monoxide has a major absorption band at 2100 cm⁻¹ or 4.8 μm, due to unsymmetrical vibration modes.
Theoretical IR spectrum of carbon monoxide, CO. The spectrum was simulated at:
http://www.spectralcalc.com/info/about.php.
The IR spectrum of CO below shows an exhaust gas mixture from an oldtime car without catalytical cleaning. Nowadays, modern car exhaust contains mostly CO₂ and H₂O - the CO concentration is very low.
IR spectrum of 1942 Packard exhaust, showing a mixture of hydrocarbons, water, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The spectrum was found on Internet in a paper by Jane A. Ganske:
http://chemeducator.org/bibs/0008006/860353jg.htm